Cybersecurity at a glance
Reading time: 7min | Author: Lukas Dubiel| Last updated on 14.07.2024
Content of the article
- What does cybersecurity mean?
- What areas does cybersecurity cover?
- What types of cyber threats are there?
- Attacks on confidentiality
- Attacks on integrity
- Attacks on availability
- Malware
- Ransomware
- Spyware
- Trojans
- DoS or DDoS
- Phishing
- How important is cybersecurity for companies?
- What is the difference between cybersecurity and IT security?
- What challenges does cyber security pose?
- What should you look out for in cybersecurity software?
Cybersecurity has become one of the most pressing issues of our time. In a world where almost all aspects of our lives depend on technology, businesses, governments and even individuals are at constant risk of cyberattacks.
From simple phishing attempts to sophisticated ransomware attacks, the threats are varied and can have devastating effects. A successful cyberattack can not only cause financial damage, but also destroy customer trust, damage the company’s reputation and even jeopardize national security.
Therefore, it is crucial that organizations and individuals understand the importance of cybersecurity and take appropriate measures to protect themselves from cyberattacks.
What does cybersecurity mean?
Cybersecurity refers to all methods and technologies used to protect networks, computers, mobile devices and all types of data from being hacked. Cybersecurity is the generic term for all measures that help a company, an organization or a private household to protect itself from cyberattacks.
What areas does cybersecurity cover?
Cybersecurity covers various areas and subtopics. These include:
- Network security
- Data protection and data security
- Endpoint security
- Thread response
- E-mail security
- Cloud security
- Identity Access Management
Cybersecurity is a very vague generic term. The infrastructure in a company where cybersecurity solutions are in demand can be divided into three areas. The network, the cloud and finally the endpoints.
What types of cyber threats are there?
There are many types of cyber threats that can attack devices and networks in an organization, but they generally fall into three categories: Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability attacks.
Confidentiality attacks
These attacks can be aimed at stealing personally identifiable information (PII) such as social security number, bank account number or credit card information. After these attacks, your information may be sold or traded on the dark web for others to buy and use.
Attacks on integrity
These attacks consist of personal or corporate sabotage and are often referred to as leaks. Cybercriminals gain access to sensitive information and release it in order to expose the data and cause the public to lose trust in an individual or company.
Attacks on availability
The aim of this type of cyberattack is to deny users access to their own data until they pay a fee or ransom. Typically, cybercriminals break into a network, prevent access to important data and demand payment of a ransom. Sometimes companies pay the ransom and only fix the cyber vulnerability afterwards to avoid business disruption.
Malware
Malware is the generic term for various types of cyber threats and simply means “malicious software”. Spyware, ransomware, viruses, Trojans and worms are all methods used by cyber criminals to cause damage to networks and servers of organizations. They are all grouped together under the term malware.
Ransomware
Ransomware (ransom or extortion software) is malware that paralyzes certain programs and prevents access after successfully penetrating a system or network. An attempt is then often made to extort a ransom in the form of an anonymous online payment in order to unlock access.
Spyware
Spyware is espionage software that secretly collects a user’s data without their consent or knowledge that it is being collected. The data is then sold on to third parties or used for advertising purposes.
Trojans
A Trojan is a virus that introduces other malicious scripts into a system, which in turn are intended to cause damage. The infection with a Trojan often goes unnoticed. Trojans usually work in the background and try to create security loopholes or spy on data.
DoS or DDoS
This type of cyber threat stands for (Distributed) Denial of Service. When a DDoS attack takes place, an attempt is made to overload a website or system by directing massive amounts of traffic to it. The number of requests exceeds the capacity to process these requests and the service fails.
Phishing
Phishing is a method in which a lure is sent in the form of a malicious link or attachment in an email. Phishing emails land en masse in the personal mailboxes of Internet users. By clicking on the “bait“, a script is executed or the user is redirected to a malicious website.
How important is cybersecurity for companies?
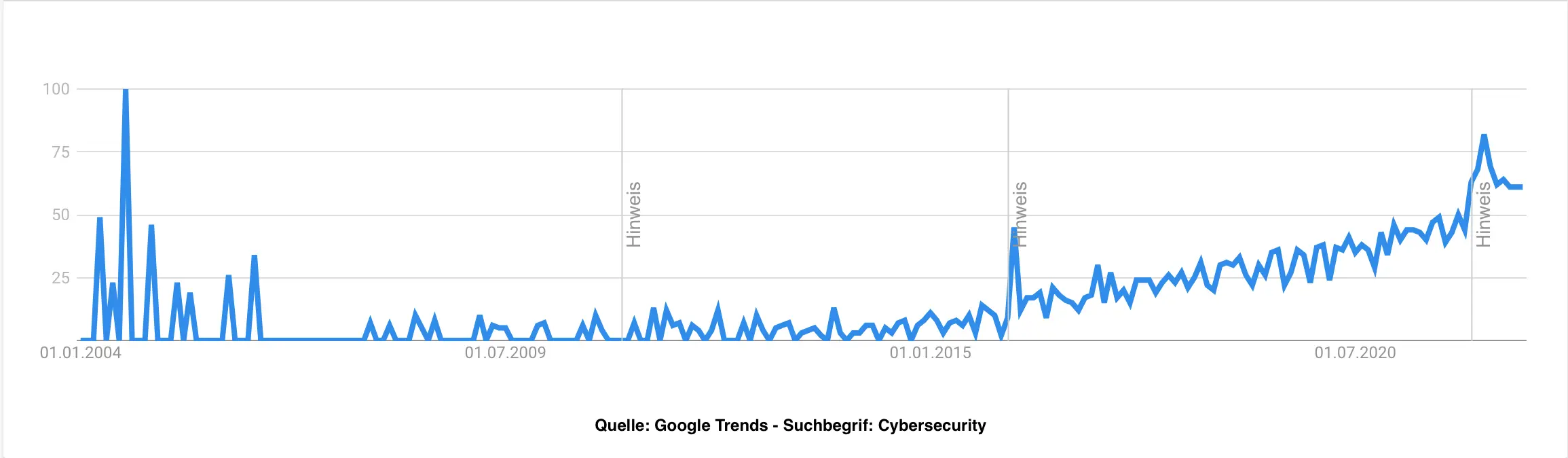
The demand for cyber security solutions has been steadily increasing in recent years. With the outbreak of war in Ukraine, this demand has once again taken an abrupt leap upwards. In this country, cyber attacks have risen sharply in recent months. Small and medium-sized companies are particularly affected. This is because, on the one hand, the financial incentives for successfully carrying out a cyber attack are high – on the other hand, many companies lack the personnel and know-how to effectively protect themselves against cyber attacks.
What is the difference between cybersecurity and IT security?
Cybersecurity and IT security mean roughly the same thing. The term IT security is a German term and is now somewhat older, while the term cybersecurity is much more modern and is used internationally.
It encompasses all technologies that help to protect against malicious software and malicious attacks from the internet.
What challenges does cyber security pose?
The cyber threat landscape is constantly evolving. Digital threats are becoming more and more complex – at the same time, the complexity of cybersecurity solutions is also increasing.
A crucial sticking point for companies is the strict legal situation when it comes to data protection and data security. Many companies now store up to 100% of their company data in the cloud. This creates new risks and threats.
The laws and regulations also restrict companies when it comes to combating cyber attacks, as many resources are outside the legal framework. An unfair game, as cyber criminals do not take this into account.
If a company becomes the target of a cyber attack, it may even be liable to prosecution. This is because legislation stipulates that in the event of misuse and theft of customer data, such incidents must be reported to a competent authority within a short period of time. Failure to do so could result in heavy fines.
What should you look out for in cybersecurity software?
First of all, a company should determine exactly what goals are to be achieved with the software. Every company has a different starting position, a different number of employees and a very specific business area that is sometimes more and sometimes less susceptible to cyber attacks.
High-quality software alone is by no means enough. It is just as important to make the right decisions at the right time in order to prevent attacks and preserve the integrity of the company network.
Do you need help with cybersecurity?
An IT service provider like jemix can help you set up a modern cybersecurity solution and is available to you as an external consultant and IT specialist. Arrange your free initial consultation today!

Have we sparked your interest?
Get in touch with us!
Contact us
