Data privacy and compliance in companies (2022) – What needs to be considered?
Content of the article
- For what and when is compliance required in the company?
- Compliance vs Data Protection – What is the difference?
- Protecting personal data through a compliance management system
- Data protection and compliance with a whistleblowing system
- Which compliance topics and areas need to be considered?
- Data protection compliance: Which data is particularly sensitive?
- What does a compliance manager or compliance officer do?
- When do you need a data protection officer?
- What are the tasks of a data protection officer?
- What is the difference between IT security and IT compliance?
You might also be interested
When we talk about data privacy and compliance, we are referring to certain guidelines that an organization must follow to ensure the security of its processes.
Each policy a company formulates then details how it handles data and digital communications. Since compliance is mostly about guidelines and not laws, there are no direct legal consequences for a violation. They are therefore primarily standards to which employees and stakeholders in a company are expected to adhere.
For what and when is compliance required in the company?
Whether a compliance system is required in the company or even prescribed by law depends on certain factors. The size of the company plays a primary role. The more employees work in a company, the more important it becomes to implement and adhere to a compliance regulation.
Whether a compliance system is necessary also depends on the industry, the type of company and whether the company is listed on the stock exchange. An IPO of the company, for example, is always accompanied by legal requirements and new obligations.
Compliance vs Data Privacy – What is the difference?
Compliance is the term for guidelines and standards that are established within a company. They differ between companies and organizations.
Data privacy is uniform within the EU. Since May 25, 2018, the corresponding law, the GDPR, applies throughout the EU.
Compliance in the company must therefore be aligned with the applicable laws. However, compliance in an organization also regulates all other important areas – not just data privacy. Differences also lie in the professions that arise from the respective fields.
The data privacy officer acts as an independent body, as a consultant. His or her task is to ensure compliance with the GDPR within the company. Compliance managers have to take care of compliance with all important guidelines in a company – from topics such as communication and handling of information, to antitrust law and corruption.
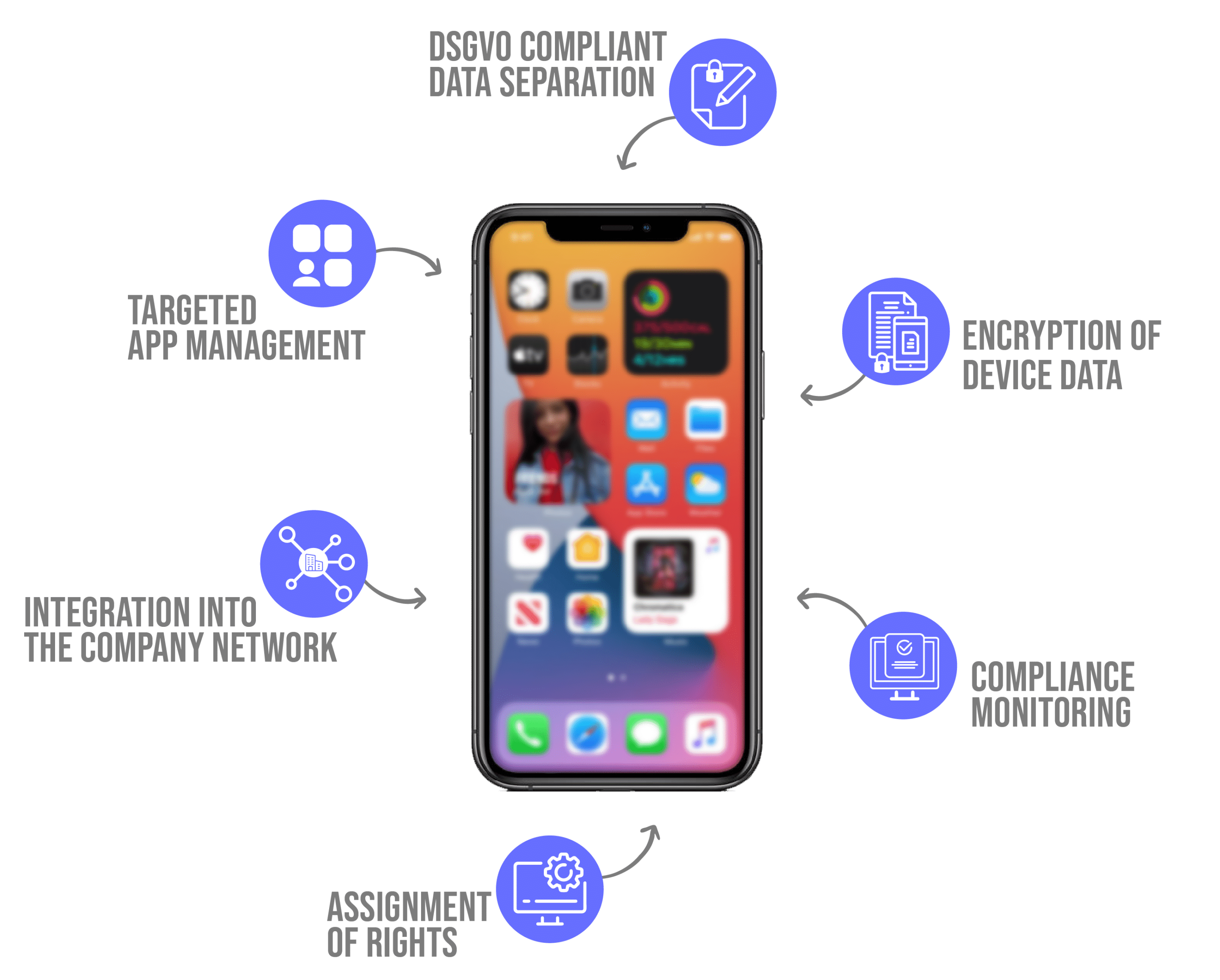
When checking and complying with the GDPR and internal compliance, many companies usually use a mobile device management (MDM) system.
Protecting personal data through a compliance management system
Many organizations have a vested interest in making sure their internal compliance works. A compliance management system helps some companies to achieve this.
Another way to ensure better compliance is through compliance training for employees.
Data privacy and compliance with a whistleblowing system
Since the end of 2021, EU legislation has included the so-called EU Whistleblowing Directive. This obliges companies in Europe to set up a whistleblowing system. The aim is to identify compliance risks and violations at an early stage through anonymous tips from whistleblowers. Whistleblower systems are therefore an integral part of corporate compliance systems.
But this only works if the identity of the whistleblower can remain secret. This is where data privacy comes into play: No matter how a company implements its whistleblower system, the personal data about the whistleblower is particularly sensitive and must therefore be protected especially well. The compliance officer should therefore sit down with data privacy officer and work out a sensible concept together.
Which compliance topics and areas need to be considered?
Compliance affects all areas of the company. In addition, other stakeholders such as customers, employees, service providers, and cooperation partners are affected. After all, they all come into contact with the company’s data privacy issues sooner or later.
Compliance programs in companies cover topics such as data privacy as well as combating corruption and money laundering. The introduction of a whistleblowing system is also a central component. Whistleblowing systems regulate the handling of compliance violations and the protection of whistleblowers who report these violations.
Data privacy and compliance: Which data is particularly sensitive?
All personal data must be protected with particular care. This means all general personal data (name, address, birthday, telephone number, etc..) plus bank data, location data, data on health insurance or social security. IP address and other location data also fall into the sensitive area.Information about property (vehicle ownership, real estate ownership, land registry entries, …) is also included. And, of course, physical data about the person’s appearance, height or health.
In the case of online companies, it is customer data about orders and purchasing behavior, account data, passwords and the address.
Data privacy compliance: Which data is particularly sensitive?
All personal data must be protected with particular care. This means all general personal data (name, address, birthday, telephone number, etc..) plus bank data, location data, data on health insurance or social security. IP address and other location data also fall into the sensitive area.

What does a compliance manager or compliance officer do?
A compliance manager is a type of data privacy officer who is used primarily in larger digitally present companies to enforce the company’s compliance and monitor compliance.
In small and medium-sized companies, there is usually only one compliance officer, while in large companies and corporations, there are entire departments with multiple compliance officers.
Companies use mobile device management software to maintain internal compliance and DSGVO. Such a solution facilitates their compliance immensely.
When do you need a data privacy officer?
According to the requirements of the EU Data Privacy Regulation, a company is obliged to appoint a data privacy officer if it has more than 20 employees who are regularly involved in the use of personal data. In doing so, it is advisable to make a written designation of the person.
However, a company is necessarily obliged to appoint a data privacy officer in some special cases, if…
- special types of personal data (e.g., about political/religious beliefs, ethnicity, sex life, health) are processed
or
- the core business of the company lies in the collection, processing or other use of personal data.
The data privacy officer is subject to a duty of confidentiality and has the right to refuse to testify. In addition, the data privacy officer is subject to special privacy against dismissal.
What are the tasks of a data privacy officer?
The central task of a data privacy officer is to check whether the provisions of data privacy law are being complied with in the handling of personal data.
He or she checks the procedures and processes in the company and ensures that compliance in the company is in line with the General Data privacy regulation.
If data privacy violations and infringements are identified, or potential risks of violation are identified, it is the task of the officer, in consultation with the management, to find solutions and rectify the errors.
What is the difference between IT security and IT compliance?
Although IT security is integrated with compliance, the two focus differently. Compliance focuses on cybersecurity, monitoring and protecting user data.
Security focuses specifically on protecting data, ensuring reliability of operations, identifying vulnerabilities, and keeping users informed of the latest trends. IT security encompasses all strategies to protect the business environment. IT compliance covers specific issues and requires organizations to put in place a defined infrastructure to protect data.
Both categories are necessary to protect data, but compliance is an issue for companies that must follow the rules closely or face hefty fines. Compliance guidelines may be strict, but they help companies learn best practices in cybersecurity and data privacy.
